Aspect Oriented Programming
관점지향 프로그래밍
스프링 어플리케이션은 대부분 특별한 경우를 제외 하고는 MVC 웹 어플리케이션에서는 Web Layer, Business Layer, Data Layer로 정의.
Web Layer: REST API를 제공하며, Client 중심의 로직 적용
Business Layer: 내부 정책에 따른 logic을 개발하며, 주로 해당 부분을 개발
Data Layer: 데이터 베이스 및 외부와의 연동을 처리
AOP는 메소드들, 특정 구역에 반복되는 로직들을 한 곳에서 몰아 코딩 할 수 있게 해준다. => 스프링 어플리케이션의 특징.

코드 실습
aop 실습을 위해 build.gradle에 의존성 추가
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-aop'package com.example.aop.controller;
import com.example.aop.dto.User;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class RestApiController {
@GetMapping("/get/{id}")
public void get(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestParam String name){
System.out.println("get method");
System.out.println("get method" + id);
System.out.println("get method" + name);
}
@PostMapping("/post")
public void post(@RequestBody User user){
System.out.println("post method :" +user);
}
}package com.example.aop.dto;
public class User {
private String id;
private String pw;
private String email;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getPw() {
return pw;
}
public void setPw(String pw) {
this.pw = pw;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", pw='" + pw + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
dto User를 만들고
get과 post에 대한 메서드를 코딩하였다.
메서드가 많아 지면 end point가 많아진다. 로그를 일일히 다 찍기 어렵기에 한 곳으로 모으는 방법이 있다. 이 때 AOP를 이용한다.
클래스를 aop로 이용하기 위해서는 @Aspect 어노테이션을 사용한다.
package com.example.aop.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class ParameterAop {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.controller..*.*(..))")
private void cut(){}
}
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.controller..*.*(..))")
private void cut(){}저 경로의 패키지에 있는 모든 메소드를 aop로 보겠다는 의미.
@Pointcut으로 룰을 설정하여 AOP로 설정할 수 있다.
복잡한 수식이 있을 수 있지만 기본적으로 특정 컨트롤러 하위로 설정하는 경우가 많다.
package com.example.aop.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class ParameterAop {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.controller..*.*(..))")
private void cut(){}
@Before("cut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
for(Object obj : args){
System.out.println("type : "+obj.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("value" + obj);
}
}
@AfterReturning(value = "cut()", returning = "returnObj")
public void afterReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object returnObj){
}
}
@Before 어노테이션을 통해 메서드가 실행하기 전에 넘어가는 argument가 무엇인지 설정할 수 있고 언제 실행할 지점도 설정할 수 있다.
@AfterReturning 어노테이션을 통해 반환 값을 설정할 수 있다. 어노테이션 안에 넣을 이름은 매칭 되어야 한다.
package com.example.aop.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class ParameterAop {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.controller..*.*(..))")
private void cut(){}
@Before("cut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
for(Object obj : args){
System.out.println("type : "+obj.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("value" + obj);
}
}
@AfterReturning(value = "cut()", returning = "returnObj")
public void afterReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object returnObj){
System.out.println("return OBJ");
System.out.println(returnObj);
}
}
package com.example.aop.controller;
import com.example.aop.dto.User;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class RestApiController {
@GetMapping("/get/{id}")
public String get(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestParam String name){
System.out.println("get method");
System.out.println("get method" + id);
System.out.println("get method" + name);
return id+ " " + name;
}
@PostMapping("/post")
public User post(@RequestBody User user){
System.out.println("post method :" +user);
return user;
}
}리턴 값이 생겼고 input 들어올 떄 get 값이 들어오고 post 할 시 user 객체의 값이 리턴된다.

@Before("cut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
for(Object obj : args){
System.out.println("type : "+obj.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("value" + obj);
}
}가 먼저 호출되어 user와 User의 value가 호출되었고
@PostMapping("/post")
public User post(@RequestBody User user){
System.out.println("post method :" +user);
return user;post method는 before를 지나 RestApiController에 들어가 찍혔고
@AfterReturning(value = "cut()", returning = "returnObj")
public void afterReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object returnObj){
System.out.println("return OBJ");
System.out.println(returnObj);retrun 오브젝트가 호출되어
값 들이 에코되어 호출된 것을 확인했다.
이렇 듯 어떤 값이 들어오고 나왔는지 AOP 구조를 통해 확인 할 수 있다.
GET METHOD도 호출해 보았다.

@Before("cut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
for(Object obj : args){
System.out.println("type : "+obj.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("value" + obj);
}
}먼저 호출되고
@GetMapping("/get/{id}")
public String get(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestParam String name){
System.out.println("get method");
System.out.println("get method" + id);
System.out.println("get method" + name);
return id+ " " + name;
}호출되어 get method가 호출되고
return 값이 호출 된 것도 확인 할 수 있다.
이런식으로 특정 중요한 부분 log를 남기고 싶다면 AOP를 활용해 남길 수 있다.
메소드 이름을 출력해보자.
@Before("cut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();컷 아래에 MethodSignature을 이용하여 어떠한 메소드를 사용했는지 화면에 출력하도록 하고 컨트롤러에 직접 출력하는 코드를 삭제하였다.
@GetMapping("/get/{id}")
public String get(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestParam String name){
return id+ " " + name;
}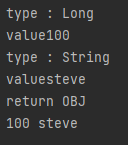
동일한 결과가 출력 된다.
이런식으로 프로그래밍을 하면 외부의 요청, 어떤 것을 return 했는지 각 메서드 별로 알 수 있기에 디버깅을 하며 따라가며 어느 부분이 오류가 났는지 파악하기 쉽다.
'Spring > Spring 공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 6. Spring Boot Annotations (0) | 2022.07.03 |
|---|---|
| 5. ObjectMapper (0) | 2022.07.02 |
| 4. AOP 코딩 실습-2 (0) | 2022.07.02 |
| 2. IOC 코드 실습 (1) | 2022.07.01 |
| 1. IoC, DI/ DI 관련 코드 실습 (1) | 2022.06.30 |


